Configuring Your Own Algorithms¶
This section describes how users can configure their own algorithms using Delphix’s built-in algorithm frameworks.
Algorithm Settings¶
The Algorithm tab displays algorithm Names along with Type and Description. This is where you add (or create) new algorithms. The default algorithms and any algorithms you have defined appear on this tab.
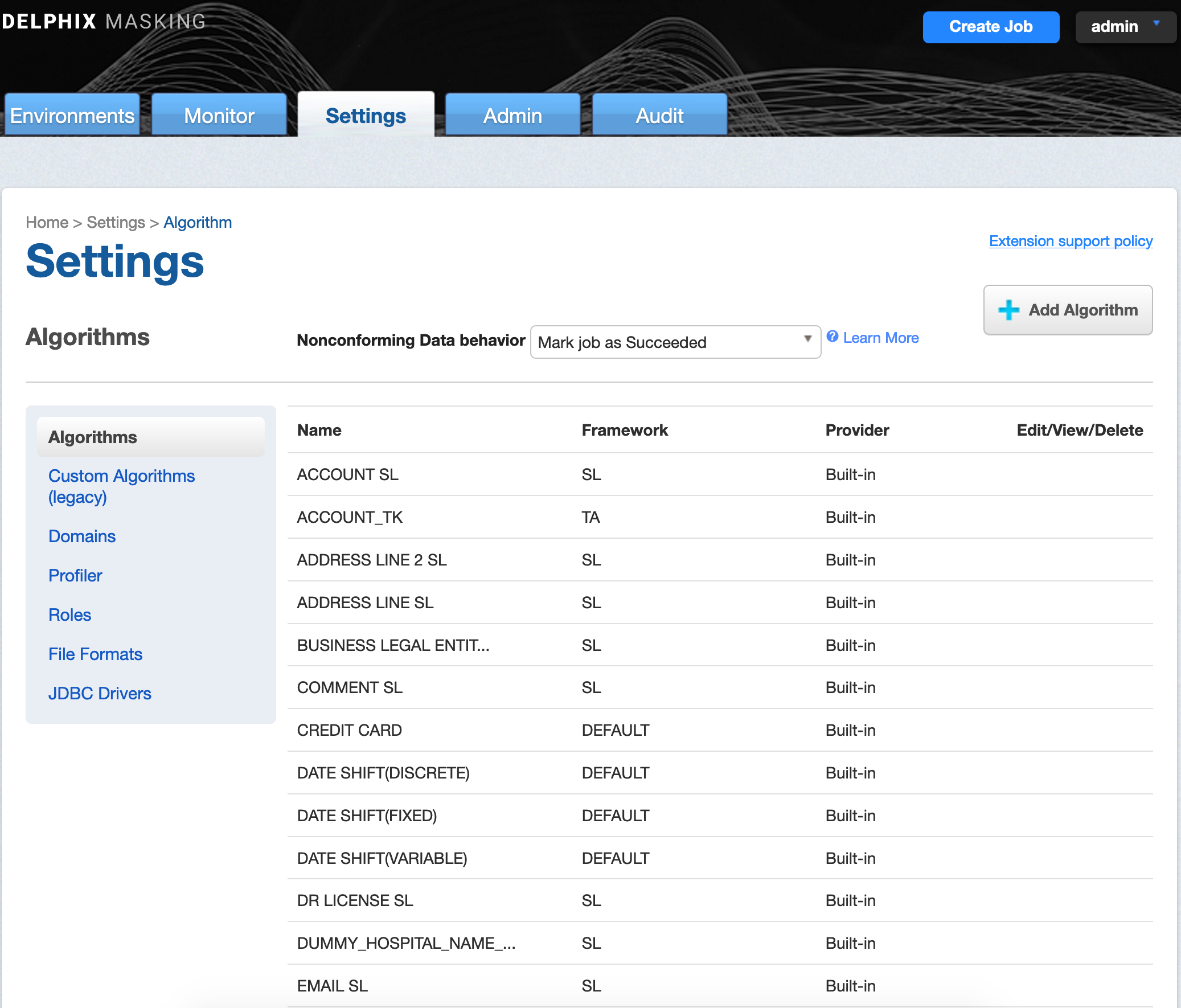
At the top of the page, If Nonconforming data is encountered is displayed to specify how all algorithms should behave if they encounter data values in an unexpected format. Mark job as Failed instructs algorithms to throw an exception that will result in the job failing. Mark job as Succeeded instructs algorithms to ignore the non-conforming data and not throw an exception. Note that Mark job as Succeeded will result in the nonconforming data not being masked should the job succeed, but the Monitor page will display a warning that can be used to report the nonconforming data events.
Creating New Algorithms¶
If none of the default algorithms meet your needs, you might want to create a new algorithm.
Algorithm Frameworks give you the ability to quickly and easily define the algorithms you want, directly on the Settings page. Then, you can immediately propagate them. Anyone in your organization who has the Delphix Masking Engine can then access the information.
Administrators can update system-defined algorithms. User-defined algorithms can be accessed by all users and updated by the owner/user who created the algorithm.
To add an algorithm:
-
In the upper right-hand corner of the Algorithm settings tab, click Add Algorithm.
-
Select an algorithm type.
-
Complete the form to the right to name and describe your new algorithm.
-
Click Save.
Choosing an Algorithm Framework¶
See Out Of The Box Secure Methods/Algorithms for a detailed description on each Algorithm Framework. The algorithm framework you choose will depend on the format of the data and your internal data security guidelines.
Secure Lookup Algorithm Framework¶
To add a secure lookup algorithm via UI:¶
-
In the upper right-hand corner of the Algorithm tab, click Add Algorithm.
-
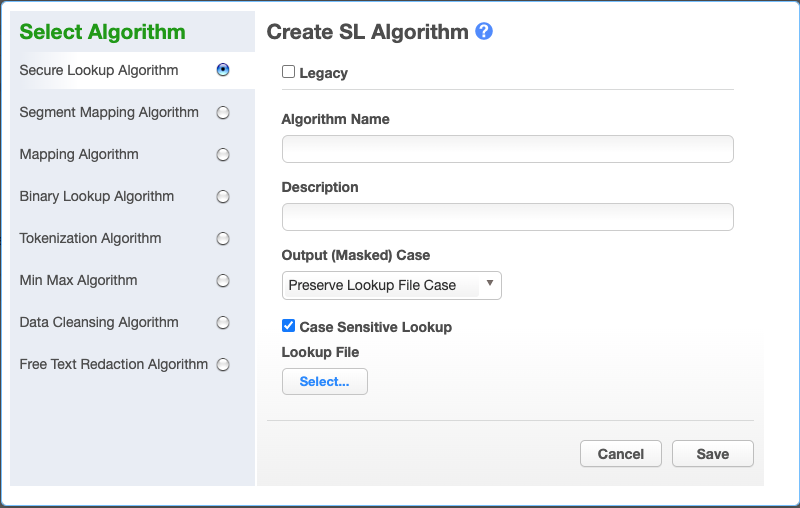
Choose Secure Lookup Algorithm. The Create SL Algorithm pane appears.

-
Choose the type of SL algorithm framework to use. For Legacy one click on
Legacybutton at the top. The default version is the newer Extended SL Framework, allowing configuration of the following options:Output (Masked) Case Case Sensitive Lookupwhich are disabled for Legacy SL Framework type.
-
Enter an Algorithm Name.
Info
This MUST be unique.
-
Enter a Description.
-
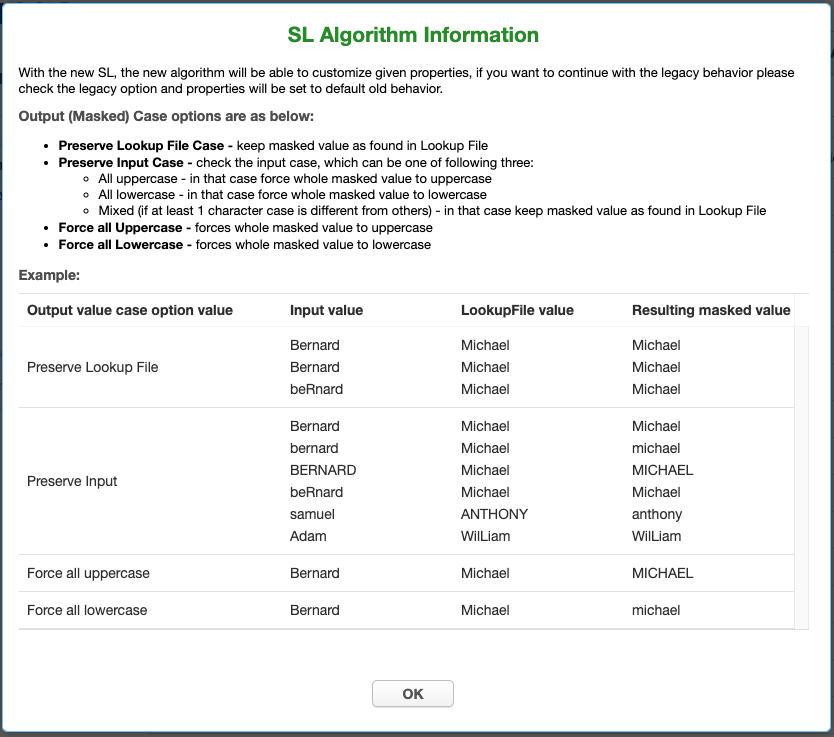
Choose the Output (Masked) Case configuration. This option is available only for the Extended SL Framework type. It is explained with the examples in the information popup window, which may be opened by clicking on the blue question sign on the above Create SL Algorithm window:
-
Choose the Case Sensitive Lookup configuration. This option is available only for the Extended SL Framework type.
If Case Sensitive Lookup box is marked then the same input of different cases will be masked to the different values. For example:
Peter -> John peter -> AndrewIf that setting is not marked (which is a default option), then lookup would be case insensitive, for example:
Peter -> John peter -> John -
Specify a Lookup File.
This file is a single list of values. It does not require a header. Every line of the Lookup File might be used as a masked value. The Lookup File must be ASCII or UTF-8 encoding compatible. The following is sample file content:
Smallville Clarkville Farmville Townville Cityname Citytown Towneaster -
When you are finished, click Save.
-
Before you can use the algorithm in a profiling job, you must add it to a domain.
Info
For Legace Framework type only: If the lookup file contains foreign alphabet characters, the file must be saved in UTF-8 format with no BOM (Byte Order Marker) for the Masking Engine to read the Unicode text correctly. Some applications, e.g. Notepad on Windows, write a BOM (Byte Order Marker) at the beginning of the Unicode file. This character will be included as part of the first replacement value, potentially leading to SQL update or insert errors on databases where this character is not allowed in VARCHAR fields - when trying to run a masking job that applies a Secure Lookup algorithm that has been created based on a UTF-8 file that included a BOM.
Extended builtin SL Framework filters the BOM automatically without causing the mentioned errors.
To add an Extended Secure Lookup Algorithm via API EndPoint:¶
-
Find the FrameworkId for the Extended SL Framework. That might be done via the following EndPoint:
algorithm GET /algorithm/frameworksPlugin name is dlpx-core, the framework name is Secure Lookup.
-
Upload Lookup File via the following EndPoint:
fileUpload POST /file-uploadsAlternatively, the Lookup File might also be provided via HTTP / HTTPS / NFS mount URLs.
-
Create an Extended SL Algorithm via the following EndPoint:
algorithm POST /algorithmsUsing the JSON formatted input, similar to the following example:
{ "algorithmName": "demoExtendedSL", "algorithmType": "COMPONENT", "frameworkId" : 1, "algorithmExtension" : { "lookupFile" : { "uri":"delphix-file://upload/f_7984ee9672b44e309f7ef5940f856e7c/ColorsLF.txt" }, "inputCaseSensitive" : true, "maskedValueCase" : "ALL_LOWER" } }Fields description:
"algorithmName" - customer created algorithm name
"algorithmType" - should be "COMPONENT" for Extended Algorithms
"description" - free text
"frameworkId" - the numeric value found in #1 above
"algorithmExtension" - the composite field, containing algorithm instance specific configuration parameters. For details see Extended builtin SL Algorithm Extension
Character Mapping Algorithm Framework¶
-
In the upper right-hand region of the Algorithm tab under Settings, click Add Algorithm.
-
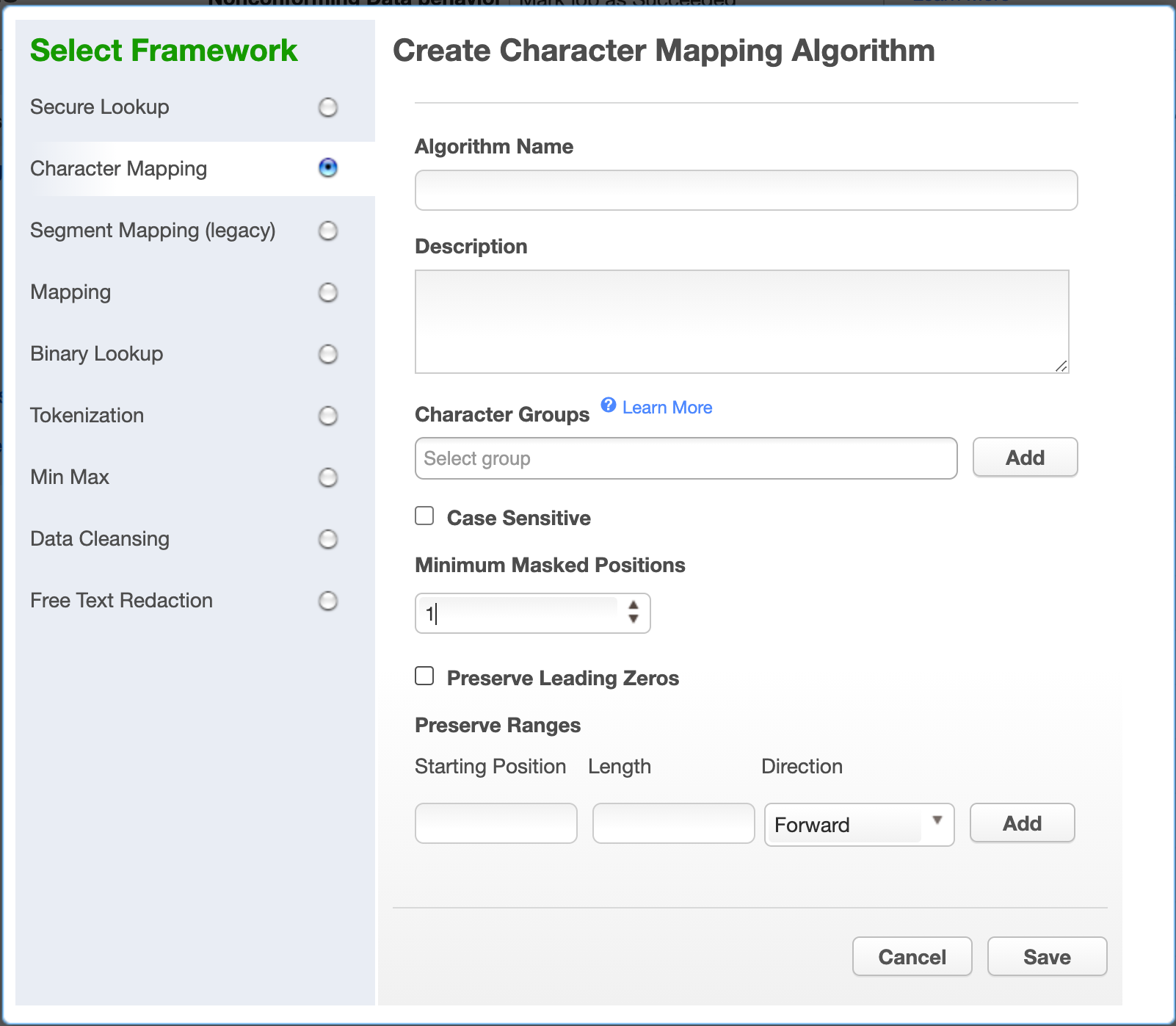
Select Character Mapping Algorithm. The "Create Character Mapping Algorithm" pane appears.
-
Enter an Algorithm Name.
Info
This MUST be unique.
-
Enter a Description.
-
Define Character Groups for each group of characters among which you would like to map. Each group may defined either by specifying each literal character in the group, such as "0123456789", or using Java Regular Expression style character ranges, such as "[0-9]". The algorithm will freely map characters to other characters within the same group, so by defining groups "[0-9]" and "[A-Z]", numbers would be replaced by other numbers, and letters by other letters, but a number would never be replaced by a letter. Groups should not contain duplicate characters, and each character may belong to only one group. Any character that is not assigned to a group will be preserved (not masked) by the algorithm.
The box below the entry area allows selection of character groups defined for other, preexisting Character Mapping algorithms.
-
Check the Case Sensitive box to cause the algorithm to treat upper and lower case characters as distinct characters for mapping.
-
Select a value for Minimum Masked Position, which sets the minimum number of characters that the algorithm must mask; fewer positions triggers non-conforming data handling. Null, empty, and all-whitespace values never trigger non-conforming data handling.
-
Check the Preserve Leading Zeros box to cause the algorithm to preserve any number of '0' characters at the beginning of each input. This is only useful if '0' has been assigned to a character group in step 5.
-
If desired, define ranges of the input value to ignore using the Preserve Ranges controls. For Character Mapping algorithms, only characters that would otherwise be masked count when determining position for preserve ranges. Each preserve range is defined by:
- Start Position - The position at which to start preserving, starting from 0.
- Length - The number of characters to preserve.
- Direction - The direction, either forward or reverse, determining whether to process from the beginning or end of input for this range.
Warning
Be wary of the following Preserve Range processing differences between Segment Mapping and Character Mapping: Segment Mapping ranges start with index 1, while Character Mapping ranges begin with index 0. Segment Mapping includes perserved characters when determining position, while Character Mapping only counts maskable characters. For example, to ignore the first two characters, you would enter Starting Position 0 for Character Mapping, but Starting Position 1 for Segment Mapping. If both algorithms were configured to preserve "-", and preserve the first two positions, Character Mapping might mask "--0000" to "--0073", while Segment Mapping might mask "--0000" to "--4638".
Segmented Mapping Algorithm Framework¶
-
In the upper right-hand region of the Algorithm tab, click Add Algorithm.
-
Select Segment Mapping Algorithm. The Create Segment Mapping Algorithm pane appears.
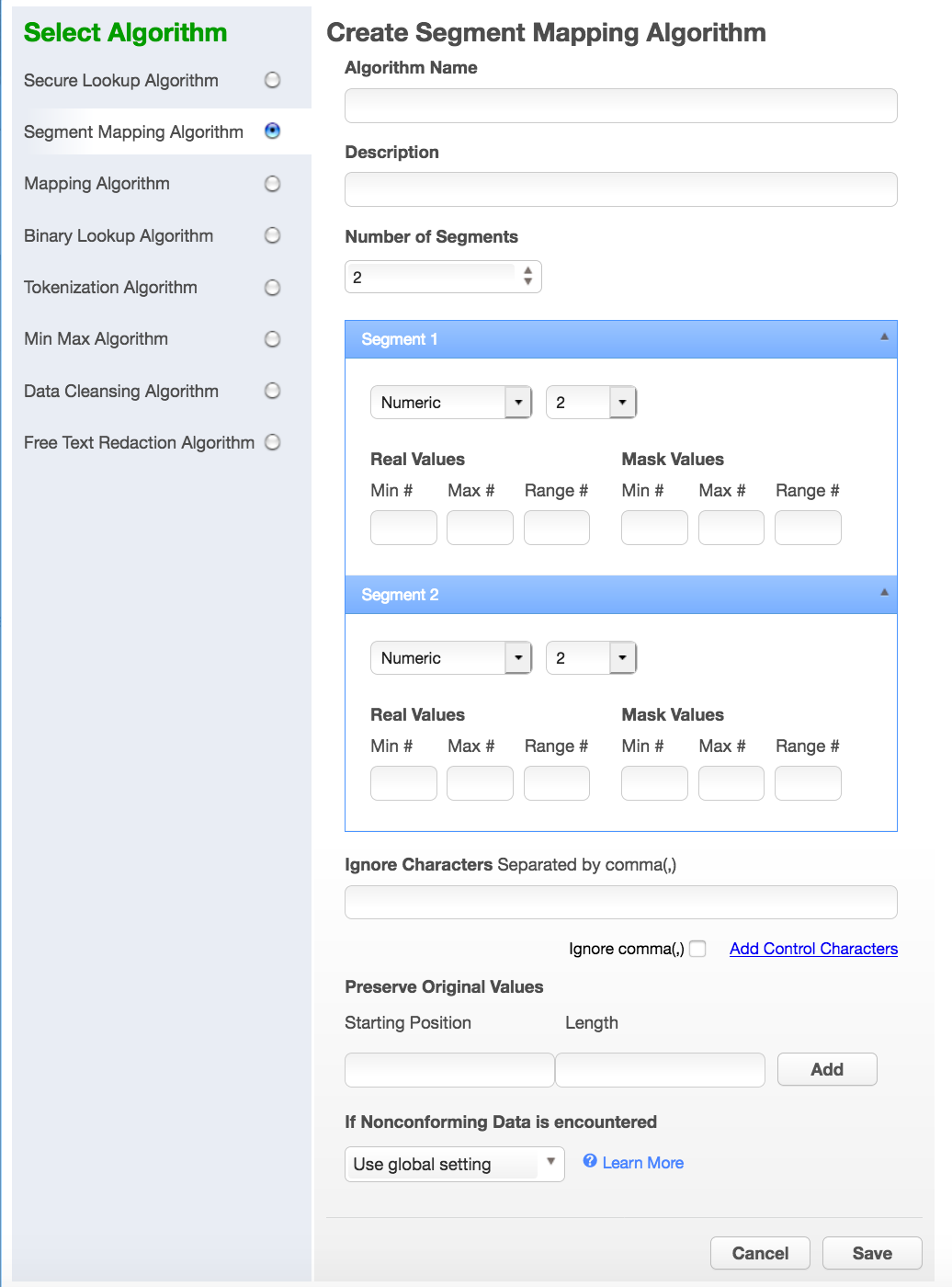
-
Enter an Algorithm Name.
Info
This MUST be unique.
-
Enter a Description.
-
From the No. of Segment drop-down menu, select how many segments you want to mask.
NOTE
This number does NOT include the values you want to preserve.
The minimum number of segments is 2; the maximum is 9. A box appears for each segment.
-
For each segment, choose the Type of segment from the drop-down: Numeric or Alphanumeric.
Info
Numeric segments are masked as whole segments. Alphanumeric segments are masked by individual characters.
-
For each segment, select its Length (number of characters) from the drop-down menu. The maximum is 4.
-
Optionally, for each segment, specify range values. You might need to specify range values to satisfy particular application requirements, for example. See the details below.
-
Preserve Original Values by entering Starting position and length values. (Position starts at 1.) For example, to preserve the second, third, and fourth values, enter Starting position 2 and length 3.
If you need additional value fields, click Add.
-
To override the behavior of the segment mapping algorithm when it encounters data values in an unexpected format, you can change the selection under If Nonconforming data is encountered. By default, the segment mapping algorithm will Use global setting as specified on the Algorithm Settings page. Selecting Mark job as Failed will instruct the segment mapping algorithm to throw an exception that will result in the job failing. Selecting Mark job as Succeeded will instruct the segment mapping algorithm to ignore the non-conforming data and not throw an exception. Note that Mark job as Succeeded will result in the nonconforming data not being masked should the job succeed, but the Monitor page will display a warning that can be used to report the nonconforming data events.
-
When you are finished, click Save.
-
Before you can use the algorithm in a profiling job, you must add it to a domain. If you are not using the Masking Engine Profiler to create your inventory, you do not need to associate the algorithm with a domain.
Specifying Range Values¶
You can specify ranges for Real Values and Mask Values. With Real Values ranges, you can specify all the possible real values to map to the ranges of masked values. Any values NOT listed in the Real Values ranges would then mask to themselves.
Specifying range values is optional. If you need unique values (for example, masking a unique key column), you MUST leave the range values blank. If you plan to certify your data, you must specify range values.
When determining a numeric or alphanumeric range, remember that a narrow range will likely generate duplicate values, which will cause your job to fail.
-
To ignore specific characters, enter one or more characters in the Ignore Character List box. Separate values with a comma.
-
To ignore the comma character (,), select the Ignore comma (,) checkbox.
-
To ignore control characters, select Add Control Characters. The Add Control Characters window appears.
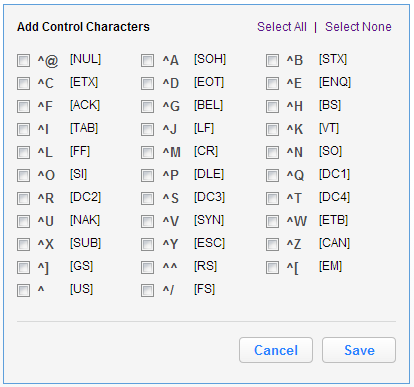
-
Select the individual control characters that you would like to ignore, or choose Select All or Select None.
-
When you are finished, click Save.
-
You are returned to the Segment Mapping pane.
Numeric Segment Type¶
-
Min# — A number; the first value in the range. Value can be 1 digit or up to the length of the segment. For example, for a 3-digit segment, you can specify 1, 2, or 3 digits. Acceptable characters: 0-9.
-
Max# — A number; the last value in the range. The value should be the same length as the segment. For example, for a 3-digit segment, you should specify 3-digits. Acceptable characters: 0-9.
-
Range# — A range of numbers; separate values in this field with a comma (,). Value should be the same length as the segment. For example, for a 3-digit segment, you should specify 3 digits. Acceptable characters: 0-9.
Info
If you do not specify a range, the Masking Engine uses the full range. For example, for a 4-digit segment, the Masking Engine uses 0-9999.
Alphanumeric Segment Type¶
-
Min# — A number from 0 to 9; the first value in the range.
-
Max# — A number from 0 to 9; the last value in the range.
-
MinChar — A letter from A to Z; the first value in the range.
-
MaxChar — A letter from A to Z; the last value in the range.
-
Range# — A range of alphanumeric characters; separate values in this field with a comma (,). Individual values can be a number from 0 to 9 or an uppercase letter from A to Z. (For example, B,C,J,K,Y,Z or AB,DE.)
Info
If you do not specify a range, the Masking Engine uses the full range (A-Z, 0-9). If you do not know the format of the input, leave the range fields empty. If you know the format of the input (for example, always alphanumeric followed by numeric), you can enter range values such as A2 and S9.
Warning
The Segment Mapping pattern and sub-patterns need to match the data in order for it to be masked. If the data is longer than the defined pattern it will be passed through unmasked. To avoid this unwanted behavior - patterns (segments), Ignore Characters, and Preserve Original Values should be set to match the data.
Mapping Algorithm Framework¶
To add a mapping algorithm:
-
In the upper right-hand corner of the Algorithm tab, click Add Algorithm.
-
Select Mapping Algorithm.
-
The Create Mapping Algorithm pane appears.
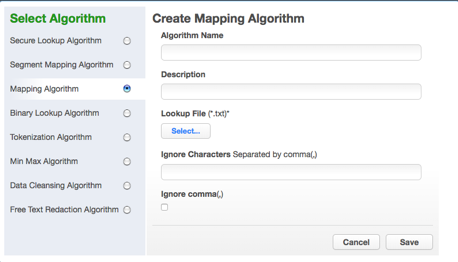
-
Enter an Algorithm Name.
Info
This MUST be unique.
-
Enter a Description.
-
Specify a Lookup File.
-
The value file must have NO header. Make sure there are no spaces or returns at the end of the last line in the file. The following is sample file content. Notice that there is no header and only a list of values.
Smallville Clarkville Farmville Townville Cityname Citytown Towneaster -
To ignore specific characters, enter one or more characters in the Ignore Character List box. Separate values with a comma.
-
To ignore the comma character (,), select the Ignore comma (,) checkbox.
-
When you are finished, click Save.
Before you can use the algorithm by specifying it in a profiling job, you must add it to a domain. If you are not using the Masking Engine Profiler to create your inventory, you do not need to associate the algorithm with a domain.
Masking Binary Lookup Algorithm Framework¶
To add a binary lookup algorithm:
-
At the top right of the Algorithm tab, click Add Algorithm.
-
Select Binary Lookup Algorithm. The Create Binary SL Algorithm pane appears.
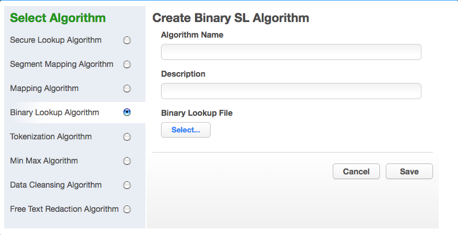
-
Enter an Algorithm Name.
Info
This MUST be unique.
-
Enter a Description.
-
Select a Binary Lookup File on your filesystem.
-
Click Save.
Tokenization Algorithm Framework¶
To add a Tokenization algorithm:
-
At the top right of the Algorithm tab, click Add Algorithm.
-
Select Tokenization Algorithm. The Create Tokenization Algorithm pane appears.
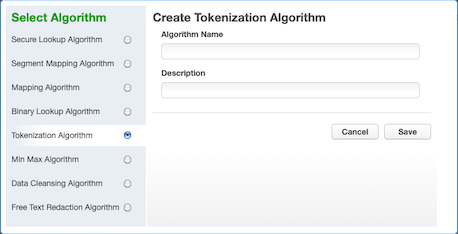
-
Enter an Algorithm Name.
Info
This MUST be unique.
-
Enter a Description.
-
Click Save.
Once you have created an algorithm, you will need to associate it with a domain.
-
Navigate to the Home>Settings>Domains page and click Add Domain.
-
Enter a domain name.
-
From the Tokenization Algorithm Name drop-down menu, select your algorithm.
Next, create a Tokenization Environment:
-
On the home page, click Environments.
-
Click Add Environment.
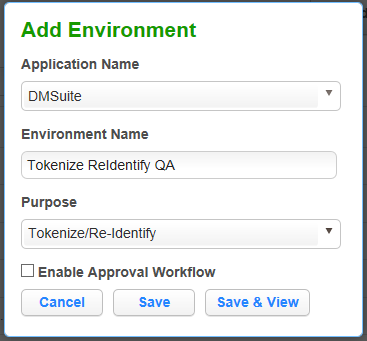
-
For Purpose, select Tokenize/Re-Identify.
-
Click Save.
Info
This environment will be used to re-identify your data when required.
-
Set up a Tokenize job using the tokenization method. Execute the job.
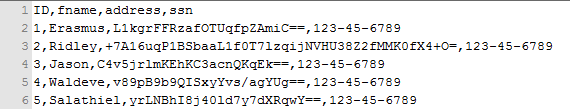
Here is a snapshot of the data before and after Tokenization to give you an idea of what it will look like.
Before Tokenization

After Tokenization
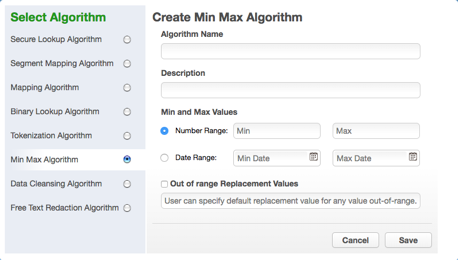
MIN Max Algorithm Framework¶
The Delphix Masking Engine provides a "Min Max Algorithm" to normalize data within a range – for example, 10 to 400. Values that are extremely high or low in certain categories allow viewers to infer someone’s identity, even if their name has been masked. For example, a salary of $1 suggests a company’s CEO, and some age ranges suggest higher insurance risk. You can use a min max algorithm to move all values of this kind into the midrange. This algorithm allows you to make sure that all the values in the database are within a specified range.
If the Out of range Replacement Values checkbox is selected, a default value is used when the input cannot be evaluated.
-
Enter the Algorithm Name.
Info
This MUST be unique.
-
Enter a Description.
-
Enter Min Value and Max Value.
-
Click Out of range Replacement Values.
-
Click Save.
Example: Age less than 18 years - enter Min Value 0 and Max Value 18.
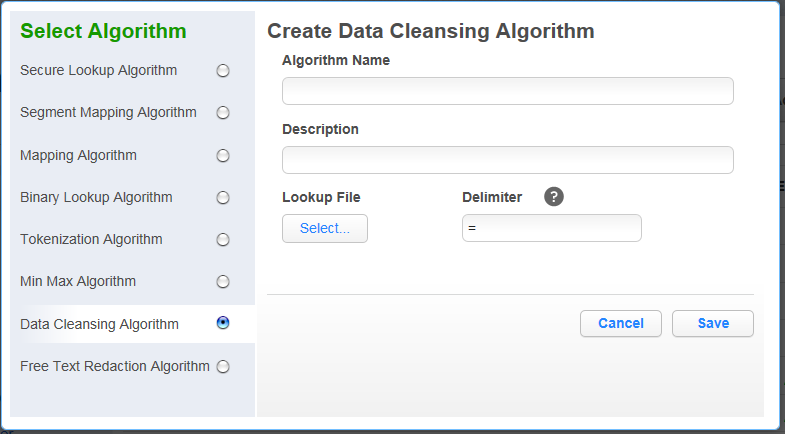
Data Cleansing Algorithm Framework¶
A data cleansing algorithm does not perform any masking. Instead, it standardizes varied spellings, misspellings, and abbreviations for the same name. For example, “Ariz,” “Az,” and “Arizona” can all be cleansed to “AZ.” Use this algorithm if the target data needs to be in a standard format prior to masking.
-
Enter an Algorithm Name.
Info
This MUST be unique.
-
Enter a Description.
-
Select Lookup File location.
-
Specify a Delimiter (key and value separator). The default delimiter is =. You can change this to match the lookup file.
-
Click Save.
Below is an example of a lookup input file. It does not require a header. Make sure there are no spaces or returns at the end of the last line in the file. The following is sample file content:
NYC=NY
NY City=NY
New York=NY
Manhattan=NY
Free Text Algorithm Framework¶
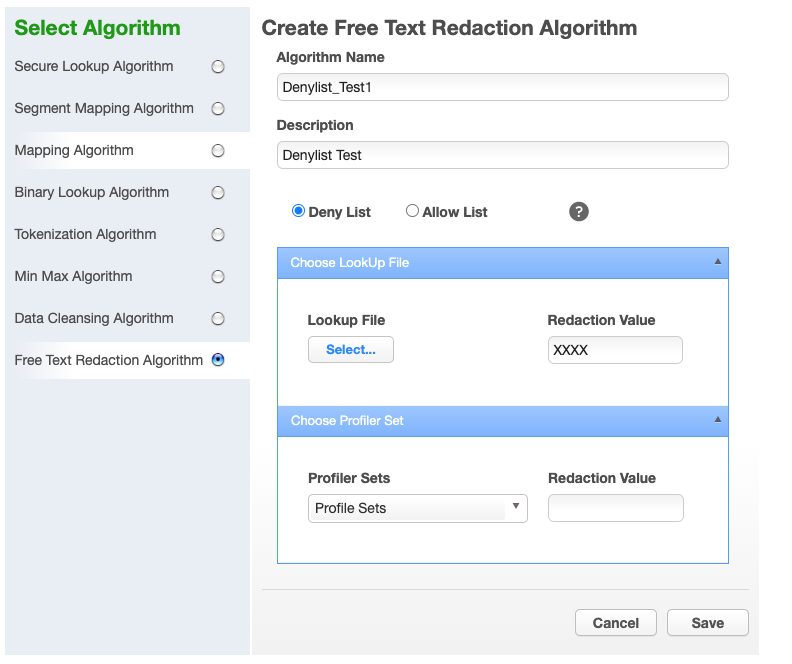
To add a free text redaction algorithm:
-
Enter an Algorithm Name.
-
Enter a Description.
-
Select the Deny List or Allow List radio button.
-
Select Lookup File and enter Redaction Value OR/AND
-
Select Profiler Sets from the drop-down menu and enter Redaction Value.
-
Click Save.
Free Text Redaction Example¶
-
Create an Input file.
-
Create an Input file using Notepad. Enter the following text:
The customer Bob Jones is satisfied with the terms of the sales agreement. Please call to confirm at 718-223-7896. -
Save the file as txt.
-
Create lookup file.
-
Create a lookup file.
-
Use Notepad to create a text file and save the file as a txt. Be sure to hit return after each field. The lookup flat file contains the following data:
Bob Jones Agreement
-
Create an Algorithm¶
You will be prompted for the following information:
-
For Algorithm Name, enter Denylist_Test1.
-
For Description, enter Denylist Test.
-
Select the Deny List radio button.
-
Select LookUp File.
-
Enter redaction value XXXX.
-
Click Save.
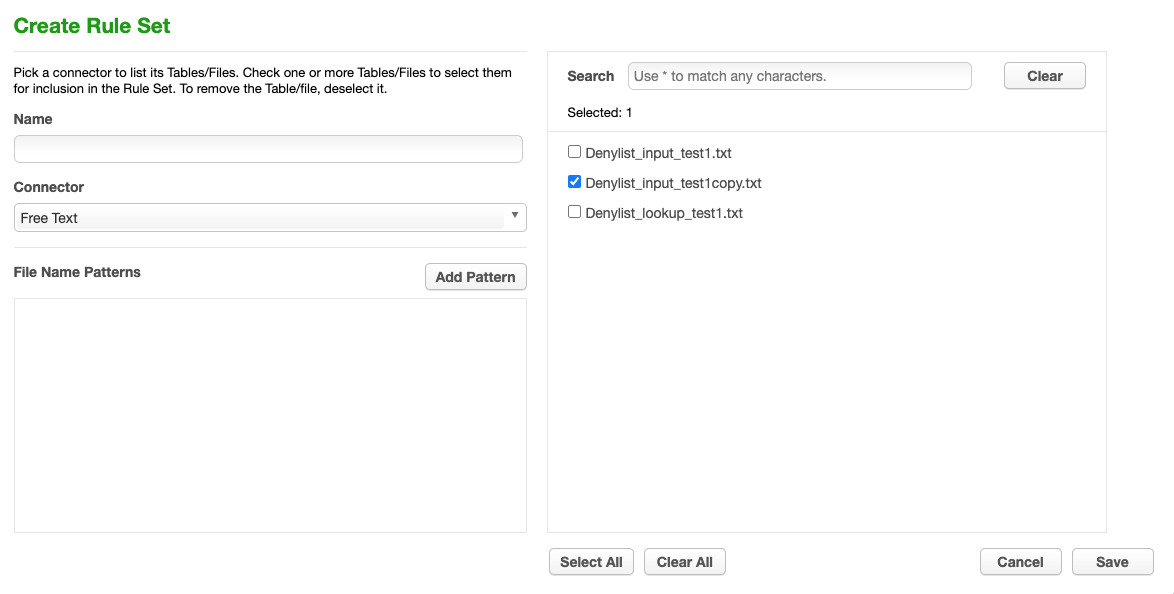
Create Rule Set¶
-
From the job page go to Rule Set and Click Create Rule Set.
-
For Rule Set Name, enter Free_ Text_RS.
-
From the Connector drop-down menu, select Free Text.
-
Select the Input File by clicking the box next to your input file
-
Click Save.
Create Masking Job¶
-
Use Free_Text Rule Set
-
Execute Masking job.
The results of the masking job will show the following:
The customer xxxx xxxx is satisfied with the terms
of the sales xxxx. Please call to confirm at 718-223-7896.
"Bob," "Jones," and "agreement" are redacted.